distributed system(computing)
What is the CAP theorem? CAP Theorem
What is the CAP Theorem? MongoDB vs Cassandra vs RDBMS, where do they stand in the CAP theorem?
https://draveness.me/consensus/
分布式系统中的Linearizability一致性的概念介绍
Introduction to the Raft algorithm
CAP Theorem for Databases: Consistency, Availability & Partition Tolerance
Making sense of the RAFT Distributed Consensus Algorithm — Part 1
Making sense of the RAFT Distributed Consensus Algorithm — Part 2
basic idea
global clock in distributed system :
- 物理: ntp 同步 多个node, 使得各个node有一样的时间
impossible: 网络延迟
- 逻辑: 全局顺序一致
what

what: use mutiple computing node to achieve some goal
advantages:
- high performace:
- reliability, fault tolerant: continue work in the presence of some faulty processes
how to implement:
- share algorithm
- replication algorithm
- central:
- master-slave
- decentral: consensus algorithm
- raft
- central:
sharing
algorithm types:
- hash
- range: [1~100]
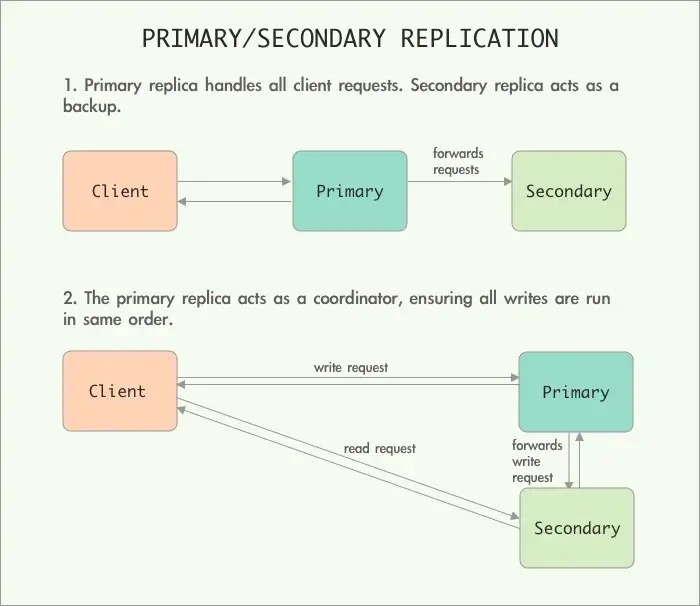
replication protocol
primary/secondary:
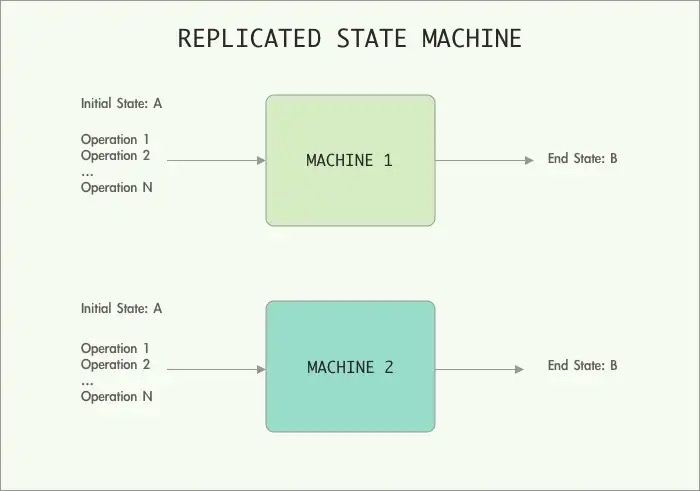
state-machine: every node have same initial state, same inputs in the same order will arrive at the same output
|
|
consitency model

what’s a model:
读取结果满足特定的排列组合,一致性越低组合越多
for example
|
|
strong:
- 线性一致性(atomic,Linearizability consistency):
- 顺序一致性(sequential )
- 因果一致性
weak feature:
- 最终一致性(eventual consistency ): 最终达到一致
weak case:
- mysql主备
Linearizability feature :
- always read the newest write
- 与全局时钟视角下一致
Linearizability case:
-
etcd

-
types? 1.
-
recent: a read must return the most recent value written;
-
the same order:
- all processor see the same order, equivalent to the global time ordering
-
顺序一致性:
- the same order:
-
因果一致性: 1.
-
最终一致性:
-
-
strict consistency: 总是返回最新值;
- 主节点先复制,再返会结果->性能降低
-
eventual consistency:最终返回最新值;
- 主节点先返回,再复制->性能高
cap
cap
- consisency: return the same data: recent data or error
- availability: all node return data
- partition tolerance: network error-> divide a network into mutiple part -> system continue work
meaning:
|
|
meaningful: 可用性和一致性存在反相关
- high consistency,less availability
- high availability,less consistency
Raft algorithm
what:
- consensus algorithm
- one of algorithm to implement state machine replication
core:
- leader election;
- log replication;
- safety
leader election
the key:
- get marjory votes
- vote when the candidate have newest log
code:
|
|



log replication
feature
- 预写日志
how
the process:
- vote: write log
- commit: leader apply
write log
|
|





safety
what: 一些属性(约束)以保证算法最终正确
list:
- leader:
- one leader: 最多选举出一个leader
- completeness: leader have all commitedIndex
- leader only can append
- log match: if log.term and log.index is same, all previous logs are identical;
- state machine safety: 同一个 index不能被apply不同的日志;
log match
log match:leader 通过比较,删除不符合的日志,补充缺少的日志 if leader.log[index].term != node.log[index].term delete node.log[index], apend leader.log[index]

sate machine safety: leader不能commit 之前任期的日志;

|
|
read
problem:
- applied index < committed index
- split brain
how:
-
转发给leader
-
wait appliedindex>=committedIndex
-
avoding split:
- read log replication
- send heartbeat, chek if mystatus== leader
- if currentTime-lastCheckTime < reElect time, not heartbeat check, else check;
-
read what? read commitIndex;
- get commited index;
- get value: when applyIndex >= commitedIndex
-
get the commiteIndex:
- who: leader;
- how:
- send heartbeart to ask for vote;
- result:
- majority votes: is leader, send commited index
- less half: not leader, send error
脑裂(brain split)
what: network error-> partition -> mutiple leader
how: 多数者投票机制
case1: 老leader 所在分区不超过半数
|
|
![[Pasted image 20221127195106.png]]
case 2: leader 所在分区 过半数。 其他分区无法选出新的leader,无法继续工作
etcd
architecture;

-
basic:
- server(http,grpc): handle request;
- raft: common algorithm;
- storage: persist data;
-
what’s wal
 write ahead log: 预写式日志;
write ahead log: 预写式日志; -
comiteIndex vs applyIndex?
- 由两个独立组件维护: raft engine: update commitedIndex; store eneign: update applyIndex,
- applyIndex <= commitedIndex
basic operation
-
get set/get:
1 2 3 4etcdctl put a b; etcdctl get a; etcdctl del a; etcd get --from-key 0; # range -
set expire;
- grant lease
- put key value –lease
1 2 3etcdctl lease grant 100 etcdctl put foo gogo --lease 12f77c78fd5f4b27 etcdctl lease keep-alive 12f77c78fd5f4b27 -
watch:
1etcd watch foo;

 write ahead log: 预写式日志;
write ahead log: 预写式日志;