mysql
Surrogate Key vs Natural Key Differences and When to Use in SQL Server
MySQL gap lock, next key lock by example
MySQL - order by 出现 using filesort根因分析及优化
The physical structure of records in InnoDB
MySQL中IS NULL、IS NOT NULL、!=不能用索引?胡扯! 带你了解 MySQL Binlog 不为人知的秘密
The basics of InnoDB space file layout
MySQL三大日志(binlog、redo log和undo log)详解
table basic
variabels
-
query variables;
1 2 3show [gloabl/session] variables; show varaibles like '%xx%'; show engines: list all engines -
set variables;
1set @@[global/session].xxxx=xxx; -
general variables
- select @@datadir: mysql data;
case sensitivity
- NO: column, index,event name;
- YES: database name, table name;
charset, collate
-
charset
- uft-8: 1-3 byte; represent BMP
emoji
- utf8mb4: 1-4byte; true utf-8; repressnt BMP and supplementary plane
- uft-8: 1-3 byte; represent BMP
-
collate: 字符集的比较和排序
- utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
- ci: case insensitivity 大小写无关
- ai:: ancent insensitivity 发音无关;
- utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
backticks
- why use
- the filed is a keyword(desc) or contain space
- why not use
- is not a sQL standard,not all RDBMS support it
key
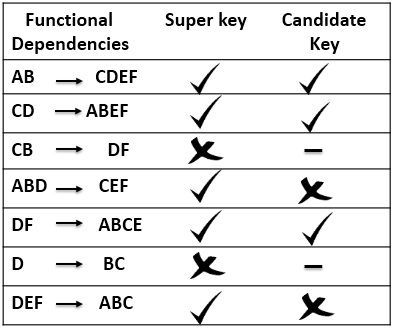
functional dependencies
- 函数依赖;x->y, 输出x,必然得出y;
- x:determinant;
- y:dependent;
super key
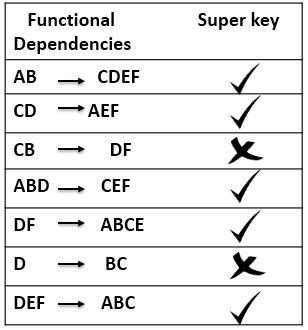
a set of field which help get rest the rest value of a row record
abcdef
if (a,b) ==> abcdef; (a,b) is the super key;
candidate key
-
what? if a super key’s proper sets have no super key;(mininal super key )

-
feature:
- unique;
-
used for?
行的标识符(row identifier)- query row
- link data in other table(foregin key)
-
types of candidate key
-
primary key: 被指定;primary
1PRIMARY KEY (`id`) -
alternate key: 未被指定为primary, 通常使用unique key标识
1UNIQUE KEY `ad_id` (`name`,`room`)
-
-
实际中一个表有多个candidate key? yes, see blow:

-
prime attribute and non-prime attribute prime/non-prime attrubute: attribute(column) in/not in candidate key;
foreign key
-
what? 在表里是候选键,在另一种不是主键, 是连接两个表的桥梁;
-
a table: id, s_id: child table
-
b table, id name: parent table
1 2# in a table; foregin key s_id reference b(id)
-
-
通常使用主键作为外键
natural key vs sugrage key
-
what? 使用哪个作为主键
- natural key:自然键,业务键,是业务里包含的字段(自然有的)作为主键;
- surrogate key: 代理键,额外新建的;
-
vs
- natural key:
- pros:
- 查询不需要额外join 操作; cons:
- 业务发生改变导致主键的重新选择:当前表重新选择主键;引用当前主键的表都要重新更新主键的值
- userTable: 社保号(primary key), usename, data,当用户没有社保号的时候,要重新选择主键,
- pros:
- surrogate key:
- pros:
- 业务变化影响小
- cons:
-
占用额外空间
-
查询需要做额外的join 操作,因为下发给client 一般是业务标识 user.order; user: userID, userID_forclient, name, order:orderID,userID,cost
select order.cost from order left join user where user.userID_forclient= xxxx;
-
- pros:
- natural key:
architecture

main part:
- server part: generate excute plan
- engine part: manage data
sql work:
- connector:
- create tcp connect
- auth
- parse (sql): ast tree
- excute plan
- call engine
store engine
what: how to manange data
compare:
-
transaction: innodb
-
row-level locker: innodb
-
left node:
-
innodb store key and row value
-
myisam store row pointer


innodb
basic structure:
- tablesapce: 存储table数据(leaf,non-leaf node),.idb file,
- innodb_file_per_table: 每个table 一个 .idb
- general tablespace: 多个table 共享一个 idb
- segment: 一个space划分成多个segment;
- extend: 64个page组成
- page
- row
|
|


raw format:


- nullable field bitmap
off page (溢出页) [data pointer]->[offset page] if record size <= innodb_page_size/2(8k); else: 1. dymamic format: 20bytes(pointer) in-page, the remaining part off page
index
what: a datastructure to speed up retrive data at the cost of extra space
b+tree


b tree: a enhanced version of avl, i/o oriented
- more keys one node ,lower height
|
|
b+tree: a enhanced version of b tree
- internal node only store key, more keys internal node, lower height
- double linked list: speed up range query
|
|
cluster index vs secondary index
clusater index: leaf node store all data;
secondary index: leaf node store key and primary key=



btree


- tree search 查找到left node;
- 在left node 顺序查询;
left most prefix

what:
a principle, select from left to right following composited index order
why:
composited key 大小 按照从左到右子key大小进行排序
example:
|
|
- where a=1 and b=1: 命中, keylength=6;
- where a=1 and c =1 : 部分命中;keylength=3;
- where b=1 and c=1: 未命中;
- > a, =b: 部分命中,keylength=3;
fileSort

- 是什么?
一种排序算法;使用较小内存对大数据进行排序;
- 分段排序;
- 合并;
- 触发场景: 未建立 索引字段进行排序;
- 如何规避: 建立索引
dataType
1. string
-
types:
- char,
- varchar
- text: text(2^16-1),mediumtext(2^24-1),longtext(2^32-1)
- blob:….
-
stroe in table: 可索引
- char: fixed; delete right space;
- varchar: variable and have extra 1-2byte to record size
-
varchar(255):
- <255:1byte + content;;
-
255: 2byte+content;
-
store out of table: 不可索引
- text: 按照指定方式编码
- blob: 没有编码
numeric
-
int
- tinyint: 2^8-1
- int
- big int
-
float:
- float
- double;
- decimal(total_Digits, digits after deciaml point)
2 time
| Data Type | “Zero” Value | other |
|---|---|---|
| DATE | ‘0000-00-00’ | |
| TIME | ‘00:00:00’ | |
| DATETIME | ‘0000-00-00 00:00:00’ | 4byte, utc1970~utc2038; |
| TIMESTAMP | ‘0000-00-00 00:00:00’ | 8byte,1000- 9999; |
| YEAR | 0000 |
- TIMESTAMP:会随着时区更新 store in utc, back from utc to the current time zone ; utc+8->utc-8; 查找: utc+8;
- datetime: 在任何时区查找都获得那个时间; utc+8-> 不变; 查找: 不变
normalization
what: conforming the norm form when desgin database why:
- minimize redesign when extending the database structure(easy extend)
- reduce anomaly: unexpected result
- 删除异常: want delete some filed but delete all field
- 更新异常: updateing result in inconsistency state
- 插入异常: can’t record when some field missed

how
how:
- the key
- the whole (candidate)key
- only the (candidate)key;
the key
- primary key,unique identification(no duplicate row)
- column(attribute) value are atomic
old:
| user_id | tags | age |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | brave,lovely | 18 |
——– update1 ———
user_info table:
| user_id | age |
|---|---|
| 1 | 18 |
user_info_relation:
| relation_id | user_id | tag |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | brave |
| 2 | 1 | lovely |
the whold key
non-prime attribute depend the whole of every candidate key
origin:
| adID | third_id | third_name | is_used |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | baidu_id1 | baidu001 | false |
update
| ad_id | third_id | is_used |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | baidu_id1 |
| third_id | third_name |
|---|---|
| baidu_id1 | baidu001 |
only the key
only depend the candiata key, have no transitive key
origin:
| studentid | state | country | age |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | cal | usa | 18 |
update:
student_info
| studentid | age | state |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18 | cal |
state_info
| state | country |
|---|---|
| cal | usa |
transaction
what: 一组操作被当做一个不可分割的整体, all success or fail
configure:
|
|
feature:
- atomic: a logic unit, all success or fail;
- consistency(correctness): conform constraints
- isolation: in concurrey condition, keep consistency read (at same leve)
- durability: once commit, won’t fail
mvcc
what: mutil-version concurrency control, 事务并发控制, read snapshot
current read :
- select for update(x lock); lock in share mode(s lock)
- update/insert/delete(x lock )
feature:
- non-blocking
- based on version number and snapshot
how it work: check row.version and trx.view.versionList
|
|

isolation(mvcc) level:
- read uncommited(dirty read): 无隔离
- read commited: (non-repeated read)
- not repeatable
- phantom read
- repeatable read
- phantom read
- serialization
read commited: read latest commited data

|
|
repatable commited:事务期间提交的事务不会被读取
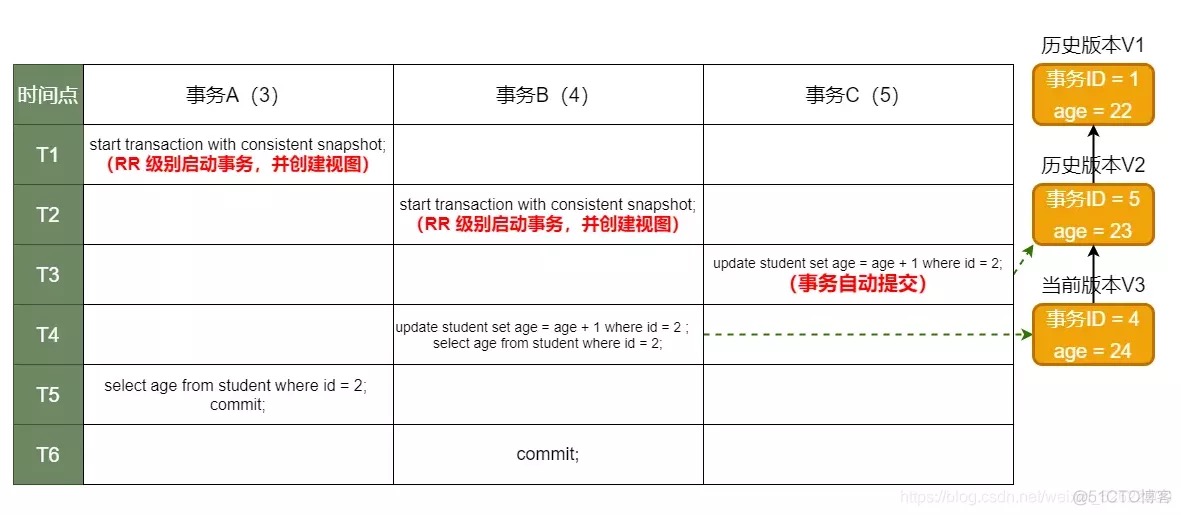
|
|
serialization: 1. what: implicitly convert all select to select…for share;
phantom
what: different result set from some query
|
|
why: 区间未加锁, 使得该区间可以任意被插入;
why: 没有
- insert:new value
- delete
- update: 更改位置,=insert ord delete;
how:
update/delete/insert会自动加加锁;
select 手动加区间锁
select...for update/share
log
types:
- redo log
- undo log
- binary log
the log be record:

- 写入undo log, 更新data,
- 写入redo log and binlog
- success: flush redo log and binlog
redo log
what: the newest change of the record; WAL(write ahead log)
content: the change of page
why need redo log:
improve random write speed,
how:
- update data
- change in memory;
- write to redo log cycle queue
- commit
- pop queue, write to os buffer;
- sync change to disk
config: select @@innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit 0. write and sync to disk every second
- write and sync to disk every trx, default
- write to os buffer every trx, sync to disk every second
![[Pasted image 20221123012043.png]]

redo log buffer structure:

undo log
what: latest snapshot of a record;
for:
- rollback
- snapshot read
format: [log header, field1,value1, field2,value2 ]
log header:
- trxid
- type
- …..
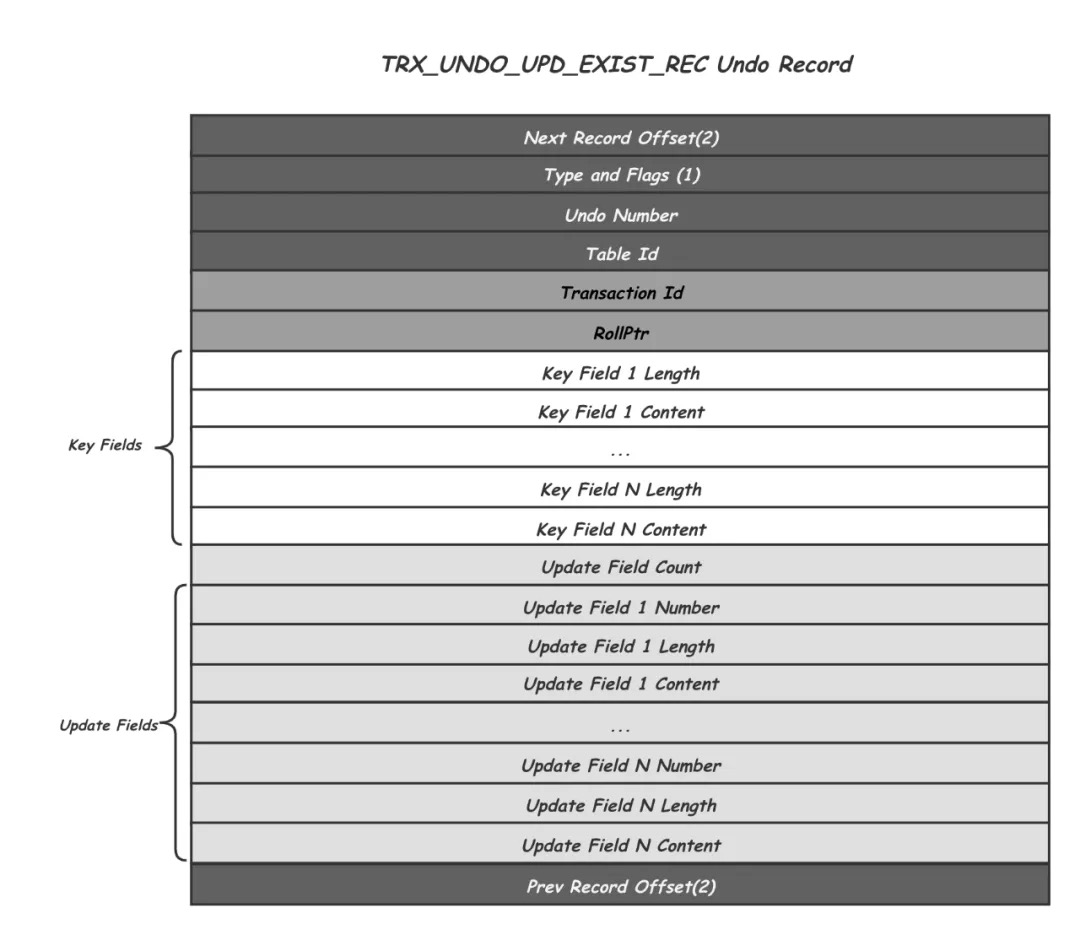
context: history snapshot

rollback: based log, inverse operation
bin log
what: the newest change of a log, operate log
for what:
- sync slave
- point-in-time recovery
content: logic
- statement: origin sql
- row: the row of every record
|
|
- mixed: both
bin vs redo log:
- conent:
- physical log
- logical log: sql
- who:
- redo: innodb
- bin: server
- use case:
config: select @@sync_binlog
-
- only write to os buffer,
-
- sync to disk every 1 trx
- n. sync to disk after n trx
point-in-time recovery
- backup data at some point
|
|
- replay from some backup postion to some postion
|
|
2 phase commit
what:
what: 确保数据一致的方法
phase:
-
request(prepare) write redo log to disk, redo log.stateu = prepare write bin log disk
-
commit() redolog.staute= commit;
-
两阶段提交
binlog 与redo log数据一致性; redo log 从prepare 更新为 comit 过程;
- write redo log, statue = prepare;
- write binlog
- update redo log statue = commit;
crash save:
- if redo log statue=commit, recover
- if redo log status= prepare, query log in bin log by trxID,if find, status= commit, recover;
Locker
types:
- table-level locks
- table locks
- intention locks
- row-level locker
- record-lock: lock a row, for updating row concurrency
- range lock: lock a range, for solving phantom read;
- gap locker: (…. );
- next-key locker:(….];
- insert intention lock (…..): 较少与其他插入的锁冲突
table locker:
|
|
table intension lock: a lock before row-level lock, allow or forbid table lock; 协调表锁和行锁
2 phase:
- locker when update/delete/insert, or select xx for update/share mode
- unlock: commit;
row-level lock
types:

how row-level lock work: secondary index and cluster index

when add range lock, curent read rules
- unique index, select where id=1
- row exist: lcok record id=1
- row not exist: (pre, after )
- not unique index, select where age=1;
- row exist: (pre, 1], (1, after)
- row not exist: (pre, after)
range example:
|
|
next key list: (-inf, 1] , (1,3] , (3,5], (5,+inf)
select * from gap wheree num=3 lock in share mode: (1 ,3] + (3,5)selct * from gap gap where id =4 lock in share mode: (3,5)
dead lock
what: 互相持有对方需要的资源(锁)
how to solve: before:
- write good sql:
- divide big tx into small
- reduce gap lock times
- update exist data;
- update by primary key
runniong:
- out log
|
|
case1
![[Pasted image 20221118221944.png]]
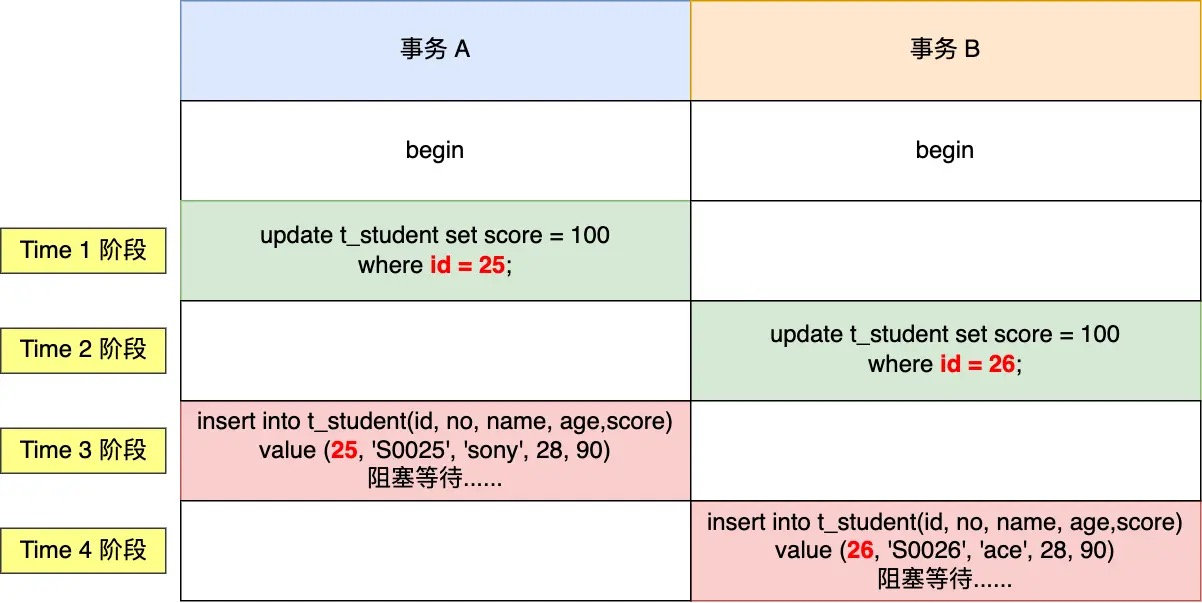
|
|
case2
![[Pasted image 20221118224931.png]]
![[Pasted image 20221118224942.png]]
|
|
优化
- moniter
- basic principle
monitor
1. slow log
-
variables:
1 2 3long_query_time slow_query_log on/off log_queries_not_using_indexes on/off
1. explain
excution plan:
|
|
-
how:
- row: less
- type: use index
-
type
-
全量扫描 ALL: 扫描主索引 index: 扫描二级索引;
-
命中索引
- ref: 等值查询索引, =
- range: 范围查询索引,< , >
- const: 查询唯一索引或者主键;
-
-
select_type
- simple: 简单
- 复杂:
- subquery:包含子查询 subquery in select or where/having
- union: 包含联合查询
-
rows: 总扫描的行数
-
extra
- use index: covring index;
- 未使用所用index:
- order by, using filesort, extenal sort
- group by, Using temporary
索引优化
被索引到
- 基于索引字段做查询:
- where: use index
- group by,order by:
- 建立联合索引:
- use coving index: 经常查询字段加入联合索引,查询的时候只查询必要字段select(index1,index2) ;
explain using index;
- 查询遵循left most prefix原则;
- use coving index: 经常查询字段加入联合索引,查询的时候只查询必要字段select(index1,index2) ;
索引失效
-
索引上做操作: 计算function;
where b+1 >0 -
like: 前置通配符 “%tang”;
-
!= is [not] null, in(x,x,x), between 不会导致索引失效; mysql会预估
读写分离
- what? 读写分离,主从同步 读和写在不同的 主机上;
replicate
-
replicate;
 slave 通过 master的 binlog
slave 通过 master的 binlog -
how to set up;
-
master::
-
grant privilege to slave;
1GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE ON *.* TO 'replica_user'@'replica_server_ip'
-
-
slave: change master source;
1 2 3 4 5 6mysql2 > CHANGE master TO SOURCE_HOST='source_server_ip', SOURCE_USER='replica_user', SOURCE_PASSWORD='password', SOURCE_LOG_FILE='mysql-bin.000001', SOURCE_LOG_POS=899; -
mysql2 >
-
-
level:
- async;
- 半同步: 至少一个slave 写入relay log 成功
- 同步
-
主备切换
- 手动切换
load balance
-
two:
- proxy
- code: if action=query: do in slave db; else do in write master db
-
数据一致性: 无法做到强一致性
-
强制读master
- 已更新数据 标记为dirty;
- if data is in dirty, read master;
proxy
-
mysql-proxy
1 2proxy-read-only-backend-addresses=192.168.73.131 proxy-backend-addresses=192.168.73.130 -
mycat
分库分表
-
what? 将数据拆分到多个库,表中,减轻压力;
-
why:
- 分库: 减轻主机(node)压力
- 分表: 减轻表的压力
table split
-
水平 vs 垂直
- 水平:行的维度拆分
- 垂直:列的维度拆分
-
partition
- range
- list
- hash
-
case
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9create table data ( id integer primary key, status char(1), data1 varchar2(10), data2 varchar2(10) ) partition by list (status) ( partition active_data values ( 'A' ), partition other_data values(default) );
vertical
-
将不常用字段拆分
1 2 3 4 5create table data ( id integer primary key, status char(1) not null, data1 varchar2(10) not null, data2 varchar2(10) not null);1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9create table data_main ( id integer primary key, status char(1) not null, data1 varchar2(10) not null ); create table data_rarely_used ( id integer primary key, data2 varchar2(10) not null, foreign key (id) references data_main (id) );
![[Pasted image 20221118183859.png]]
![[Pasted image 20221118205755.png]] i am very sad to see you when i
good
mysql dump
how to dump:
- get souce from origin :
|
|
- dump into current
|
|
DSN
loc: determine the time.Time’s string when insert into database;
when set to loc = beijing;
insert: convert time to beijing locaiton time string, then insert it select: Interpret the time string from the database as being in Beijing’s time zone.
null in sql
the cons of use null 性能开销
- 增加存储空间,需要使用 额外一个bit 记录是否为null,但是使用非null默认值如0, “",占用空间反而更大
- 索引失效: 并不会使得索引失效
使用开销: 开发者需要额外使用 is null, not null 判断有null 的column
the pros : 在表示一些 确实没有 的数据, 如邮箱, 号码, 直接使用null 会比使用默认值更容易理解;
结论: 如果业务中确实存在一些
decimal
what’s decimal;
how:
design db
-
确定需要哪些实体
- 实体属性
- 主键
-
确定实体关系
- 1v1,1vs多,many to many
- 确定主键
-
优化
- 符合范式
- 符合 1.
primary key
是什么:是什么; 主要作为其他表的外键来建立关联
使用自然健或者代理键
自然健,natural key: 已本身已有的属性作为主键, 如身份证号 代理键: surrogate key: 新建一个属性,和业务无关,如常用的id, auto increment
建议使用代理键
- 自然健可能会经常变化, 到时候其他表也要改动
- 自建键可能很长,浪费空间
使用主键或者其他unqiue key 暴露给前端/用户
使用自增主键: cons:
- 暴露信息 1. 可能暴露业务信息:如 1001,推测用户数1000
pros:
- 不需要建立新的字段
- 查询更简单,连表可直接查询
使用其他unique key: pros:
- 不暴露信息
- primary key 更改更改不会对前端有影
cons:
- 增加查询步骤,需要先查询 primary key,再链表查询




 slave 通过 master的 binlog
slave 通过 master的 binlog