图解 Linux 文件系统
Nonblocking I/O
从内核文件系统看文件读写过程
files
图解|什么是缺页错误Page Fault
Processes and Tasks
INTRODUCTION TO THE LINUX VIRTUAL FILESYSTEM (VFS) – PART I: A HIGH-LEVEL TOUR
Linux in Depth - 文件系统及 Socket 源码解析
Linux内核Page Cache和Buffer Cache关系及演化历史
深度理解 Linux 读取文件过程!
原来8张图,就可以搞懂「零拷贝」了
Linux I/O 原理和 Zero-copy 技术全面揭秘
操作系统 I/O 全流程详解





data structure
1
2
|
openfile table:
file-> node
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
// process
struct task_struct {
// ...
/* Filesystem information: */
struct fs_struct *fs;
/* Open file information: */
struct files_struct *files;
// ...
}
struct files_struct {
// ...
struct fdtable __rcu *fdt;
// ...
}
struct fdtable {
unsigned int max_fds;
struct file __rcu **fd; /* current fd array */
unsigned long *close_on_exec;
unsigned long *open_fds;
unsigned long *full_fds_bits;
struct rcu_head rcu;
};
struct file {
struct path f_path; // a dentry and a mount point which locate this file
struct inode *f_inode; // the inode underlying this file
const struct file_operations *f_op; // callbacks to function which can operate on this file
spinlock_t f_lock;
atomic_long_t f_count;
unsigned int f_flags;
fmode_t f_mode;
struct mutex f_pos_lock;
loff_t f_pos // offset in the file from which the next read or write shall commence
struct fown_struct f_owner;
void *private_data
struct address_space *f_mapping; // callbacks for memory mapping operations
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
struct dentry {
struct hlist_bl_node d_hash; // lookup hash list
struct dentry *d_parent; // parent directory
struct qstr d_name;
struct inode *d_inode; // where the name belongs to
unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN]; // small names
const struct dentry_operations *d_op;
void *d_fsdata; // fs-specific data
struct list_head d_child; // child of parent list, i.e., our siblings
struct list_head d_subdirs; // our children
};
struct inode {
__u16 i_mode; // 模式
__u16 i_nlinks; // 链接数
__u16 i_uid; // 所属用户UID
__u16 i_gid; // 所属组ID
__u32 i_size; // 文件大小
__u32 i_atime; // 访问时间
__u32 i_mtime; // 修改时间
__u32 i_ctime; // 创建时间
__u32 i_zone[10]; // 文件数对应的数据块编号
};
|
hard link and symbolic link

soft link: 类似windows快捷方式,新文件的内容是指向原文件,原文件删除,新文件不可用
hard link: 增加了文件的innode引用数,新文件的内容就是innode, 原文件删除,新文件继续可用
disk vs sockets
- 建立映射部分是一样的实现方式
task–> private file table—> file;
- 实际的存储部分,也就是inode开始出现差异
是什么

为用户层提供i/o的统一接口;调用底层的实现(ext2,ext4);
- char: 连续字节流;键盘/鼠标
- block: 被分成很多block;disk/usb;
- socket:网络
主要数据结构
- task_struct.[files_struct].[fdtable]: openfile table;
- fdtable[n]–> file: file;
- file–> entry–> inode;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
// process
struct task_struct {
// ...
/* Filesystem information: */
struct fs_struct *fs;
/* Open file information: */
struct files_struct *files;
// ...
}
struct files_struct {
// ...
struct fdtable __rcu *fdt;
// ...
}
struct fdtable {
unsigned int max_fds;
struct file __rcu **fd; /* current fd array */
unsigned long *close_on_exec;
unsigned long *open_fds;
unsigned long *full_fds_bits;
struct rcu_head rcu;
};
struct file {
struct path f_path; // a dentry and a mount point which locate this file
struct inode *f_inode; // the inode underlying this file
const struct file_operations *f_op; // callbacks to function which can operate on this file
spinlock_t f_lock;
atomic_long_t f_count;
unsigned int f_flags;
fmode_t f_mode;
struct mutex f_pos_lock;
loff_t f_pos // offset in the file from which the next read or write shall commence
struct fown_struct f_owner;
void *private_data
struct address_space *f_mapping; // callbacks for memory mapping operations
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
struct dentry {
struct hlist_bl_node d_hash; // lookup hash list
struct dentry *d_parent; // parent directory
struct qstr d_name;
struct inode *d_inode; // where the name belongs to
unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN]; // small names
const struct dentry_operations *d_op;
void *d_fsdata; // fs-specific data
struct list_head d_child; // child of parent list, i.e., our siblings
struct list_head d_subdirs; // our children
};
struct inode {
__u16 i_mode; // 模式
__u16 i_nlinks; // 链接数
__u16 i_uid; // 所属用户UID
__u16 i_gid; // 所属组ID
__u32 i_size; // 文件大小
__u32 i_atime; // 访问时间
__u32 i_mtime; // 修改时间
__u32 i_ctime; // 创建时间
__u32 i_zone[10]; // 文件数对应的数据块编号
};
|
disk vs sockets
- 建立映射部分是一样的实现方式
task–> private file table—> file;
- 实际的存储部分,也就是inode开始出现差异
controller

cpu无法直接跟硬件直接交流,必须通过控制器
cpu(or other controller:dma…)->controller(driver)-> device;
controller
- buffer data;
- excute command;
文件读写过程


读写都是基于pageCache;
1. read
KernelBuffer From OutSide; then userBuffer From KernelBuffer
-
process 根据 descriptor table 找到对应innode;
-
innode 存储对应 pageCache;
-
pageCache != null –>直接读取 pageCache
-
pageCache =null 页缺失异常,创建pageCache,读取disk数据到pageCache;
-
copy pageCache to userCache
write(删改查)
UserBuffer To Kernel Buffer
-
..
-
..
-
pageCache != null
-
pageCache =null 页缺失异常,创建pageCache,读取disk数据到pageCache
-
更新pageCache,pageCache被标记为dirty page
———–write 返回;
此时如果断电,则刚写入会丢失!;
- 写入disk;
- 定期写会disk
- 手动调用 sync() or fsync()写入磁盘
write code
the process:
open, write , fsync
code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main()
{
char my_write_str[] = "1234567890";
char my_read_str[100];
char my_filename[] = "snazzyjazz.txt";
int my_file_descriptor, close_err;
/* Open the file. Clobber it if it exists. */
my_file_descriptor = open (my_filename, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC);
/* Write 10 bytes of data and make sure it's written */
write (my_file_descriptor, (void *) my_write_str, 10);
fsync (my_file_descriptor);
close(my_file_descriptor);
}
|
how to lookup block

data array index and composited array index
data[1~7] —> block;
data[8][1-n]—> n block;
data[8][1-n][1-n]—> n^2 block
how to add a new disk to current host
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
// 1. create partition
fdisk -l
fdisk /dev/vdb
// 2. create a specific filSystem
mkfs -t ext4 /dev/vdb1
// 3. mount (attach disk filesystem to linux file system)
mount /dev/vdb1 /data
|
create a config for permanent mount at boot time
1
2
|
/etc/fstab
/dev/xvdc1 /data ext4 defaults 0 0
|
command
- fdisk: manipulate partition table
- fdisk -l: list the partition for all disk
- df: report current file system usage
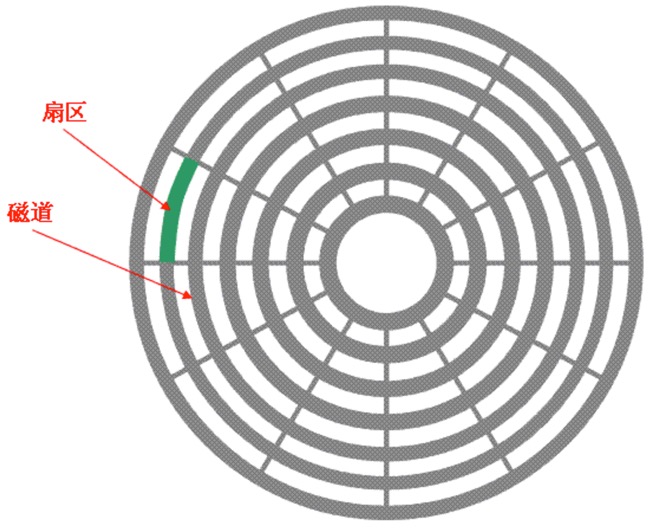
读写单位
sector(扇区):磁盘读写最小单位;
block–N个sector组成: 文件读写最小单位(内核层面;内核操作磁盘单位);
pageCache: 文件读写最小单位(用户层面;用户读写文件);


hard disk i/o



存储容量=磁头数磁道(柱面)数每道扇区数*每扇区字节数
1. 过程
- 寻道: Tseek是指将读写磁头移动至正确的磁道上所需要的时间。
- 旋转延迟: Trotation是指盘片旋转将请求数据所在的扇区移动到读写磁头下方所需要的时间
- 传输: Ttransfer是指完成传输所请求的数据所需要的时间
IOPS(input output per second) = 1000ms / (Tseek + Trotation + Transfer)
i/o优化;
- 顺序写入
- …
顺序写入(追加写);
新增数据的时候直接写在现有数据地址后面;
-
case:
wal, kafka log
-
非顺序写入消耗:
- 定位地址;
- 磁盘消耗: 寻道+旋转
-
btree是吗
不是,新增数据需要写入某个特定的page上
-
crons:
读比较麻烦;
DMA VS not DMA
1. not DMA;

cpu copy data from disk controller to kernel buffer;
- controller register-> cpu register,
- cpu regsiter to kernel buffer
2. DMA

dma controller copy data from disk controller
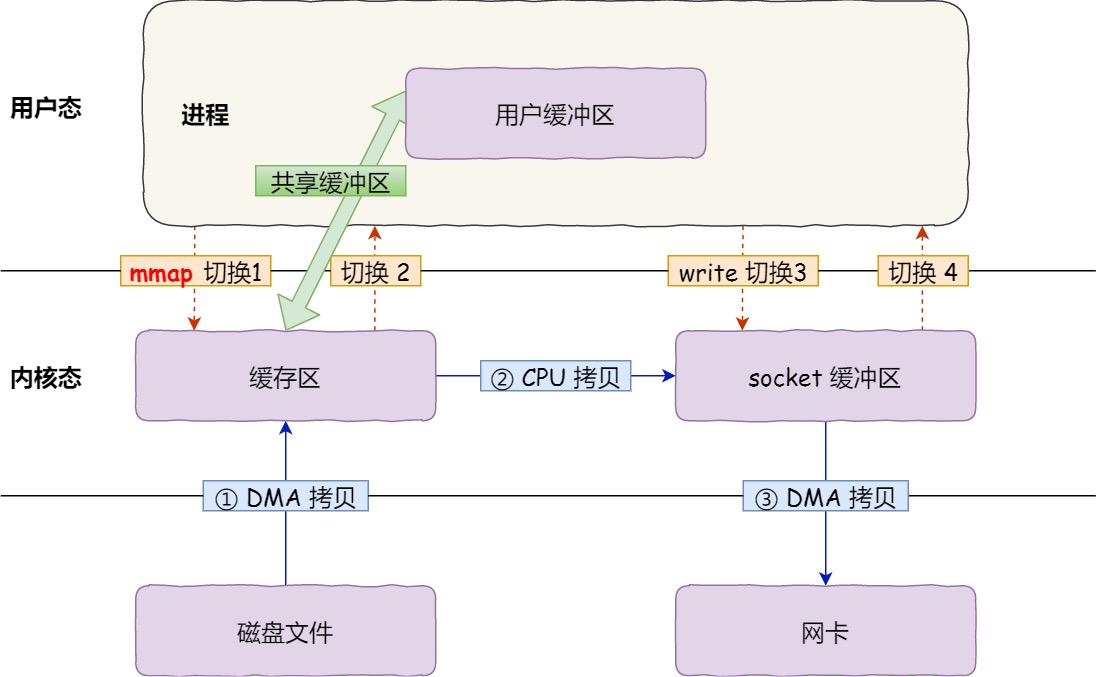
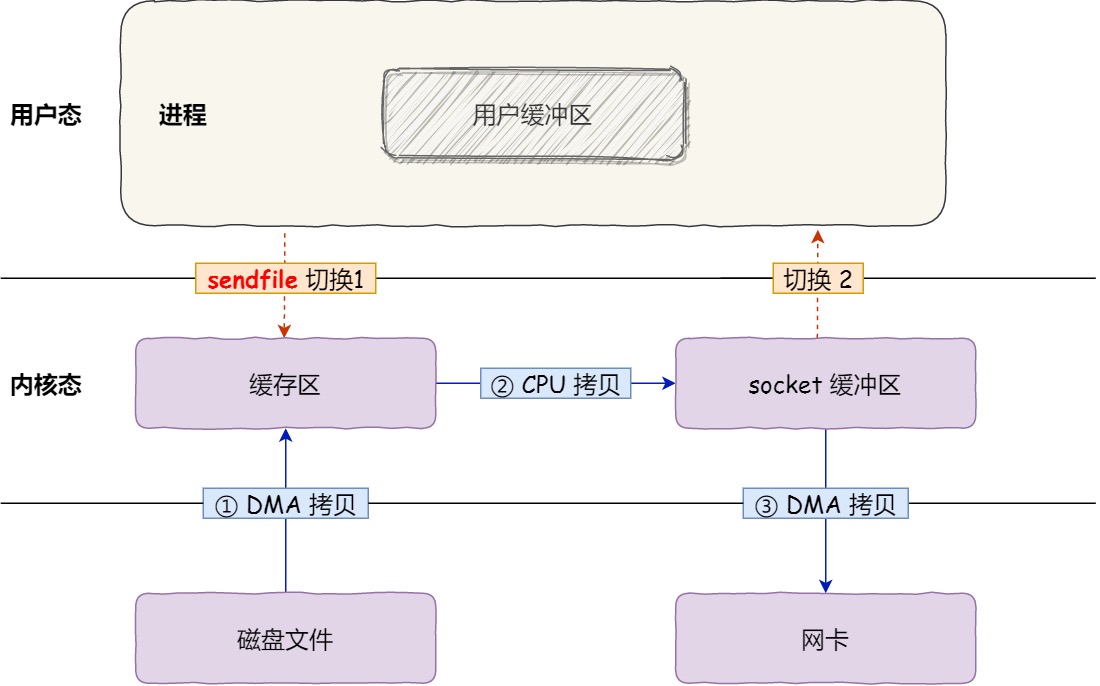
zero copy
what:
reduce data copy times
for:
improve speed of data transport
complete copy:
1
2
|
buffer = File.read
Socket.send(buffer)
|

how
mmmp
1
2
|
buf = mmap(file, len);
write(sockfd, buf, len);
|

sendfile
1
2
|
#include <sys/socket.h>
ssize_t sendfile(int out_fd, int in_fd, off_t *offset, size_t count);
|

file share
- nfs:a distributed file system protocol that allows you to share remote directories over a network.
1
|
mount -t nfs 10.10.0.10:/backups /var/backups
|
- smb:The Server Message Block protocol (
- ftp
- webdav
文件层次
- disk ; 通常代表一个真正的物理磁盘
- 分区; 对磁盘进行逻辑分区;划分分区通常是用来存储不同类型文件:系统,个人; 通过挂载集成到linux 目录;
- 文件系统: 每个分区使用一种文件系统管理 :如何管理和存储数据; ext4,xfs;
mount: 将分区上的文件系统关联到 某个目录下;