jwt
Get Started with JSON Web Tokens JSON Web Token (JWT)
jwt
what: 服务端颁发的临时id, 每次客户端拿着id访问资源,服务端需要验证是否是有效的id,
token: 临时凭证
token ways:
- cache + randomID
- valid id
jwt = payload+sigature if jwt.sigature== generateSig(payload, localKey), jwt is valid
http 是一种无状态的协议,这意味每个请求都是独立无关联的,上一次请求的状态并不能传递给下一次请求。这就导致如果没有其他机制,即使成功调用了验证请求,并不能已登验证这一状态保存到下一个请求,下一次请求仍然是未验证状态。每个需要验证的请求每次都需要自己把验证信息传送过去再验证一次。如下:/oders 和 /order/42 请求每次都需要携带验证信息。这显然是不可接受的。

session
如上所述,在没有任何优化的情况下,客户端每次请求都需要携带验证信息进行验证。我们能想到最直接优化方式就是客户端第一次验证请求之后,给客户端发放一个令牌,下一次客户端请求再携带这个令牌,服务端即认为客户端已经验证通过了,可以继续执行接下来的操作,而这正也是session的实现机制。
一直很直接的方法就是,服务端通过验证后生成一个标示id,该id对应一个用户信息,将该键值对存储在服务端内存或者文件中。然后将该id返回给客户端,用户下次请求只需要把这个id带上来,服务端检索本地存储的键值对,如能检索出相应的用户信息,即认为客户端已经验证通过,可以继续执行之后的请求。
这也是session 实现的机制,session id 存储在cookie 中,
-
session存在的问题
-
内存无限增大
-
难以水平拓展
JWT
- session 的本质
- JWT介绍
- jwt误区
session
- http无状态, 需要一个标记
session
1. session的问题
JWT
我们验证session id 其实是检索内存或者本地文件,有没有一种方式不需要
以此来验证 1. 他是有有效的 id,2. 或者他存储的用户信息如用户id
有没有一种方式,不需要去检索,只需要通过id 就能认为他是一个有效的id并且拿到对应的信息,也即这个id按照一个特定的格式编写, 我们按照特点的方式解码,如果能正确解码
jwt就规定特定格式 xxxx.xxxx.xxxx
jwt问题
- 无法中途废除
- 如果要中途废除,需要像 session一样
1. 防止别人伪造
JWT的使用
JWT的误区
JWT
jwt(json web token)
是什么?
使用base64编码的数据格式,包含三部分 xxxxx.yyyyy.zzzzz;
- header:头部信息
- payload: 主要的数据
- Signature: 签名

通过签名的方式防止数据被伪装
const token = base64urlEncoding(header) + ‘.’ + base64urlEncoding(payload) + ‘.’ + base64urlEncoding(signature) 87```
vs session
优势:
- 信息直接存储在token里
structure
| Header | { "alg" : "HS256", "typ" : "JWT" } |
Identifies which algorithm is used to generate the signatureHS256 indicates that this token is signed using HMAC-SHA256.Typical cryptographic algorithms used are HMAC with SHA-256 (HS256) and RSA signature with SHA-256 (RS256). JWA (JSON Web Algorithms) RFC 7518 introduces many more for both authentication and encryption.[8] |
|---|---|---|
| Payload | { "loggedInAs" : "admin", "iat" : 1422779638 } |
Contains a set of claims. The JWT specification defines seven Registered Claim Names which are the standard fields commonly included in tokens.[1] Custom claims are usually also included, depending on the purpose of the token.This example has the standard Issued At Time claim (iat) and a custom claim (loggedInAs). |
| Signature | HMAC-SHA256( secret, base64urlEncoding(header) + '.' + base64urlEncoding(payload) ) |
Securely validates the token. The signature is calculated by encoding the header and payload using Base64url Encoding and concatenating the two together with a period separator. That string is then run through the cryptographic algorithm specified in the header, in this case HMAC-SHA256. The Base64url Encoding is similar to base64, but uses different non-alphanumeric characters and omits padding. |
oauth 2
what: open authorization, access the user’s resoruce of other app;
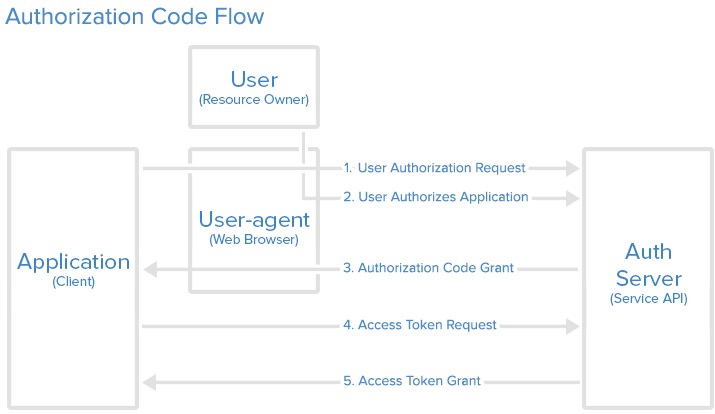
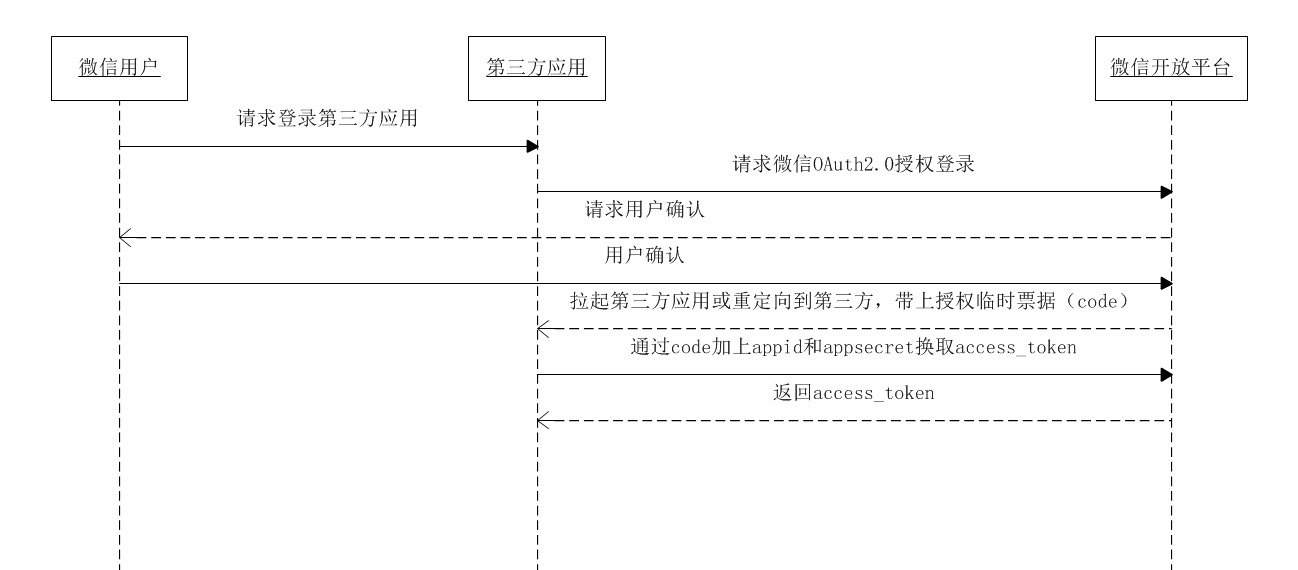
how:
- in third app: get code
- grant, send code to server’s url(redirect)
- in my app: get token
- get token by code
- access reosuce by code, then (redirect the home page)